Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Visualizing 3D model data#
Section author: Florian Zill (Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research GmbH - UFZ)
For visualizing 3D data it might make sense to plot multiple views / slices.
To create them we use pyvista as it provides all the necessary functionality.
If we want to plot multiple meshes, they have to be in a 2D numpy array.
The shape of this array determines the number of rows and columns in our plot.
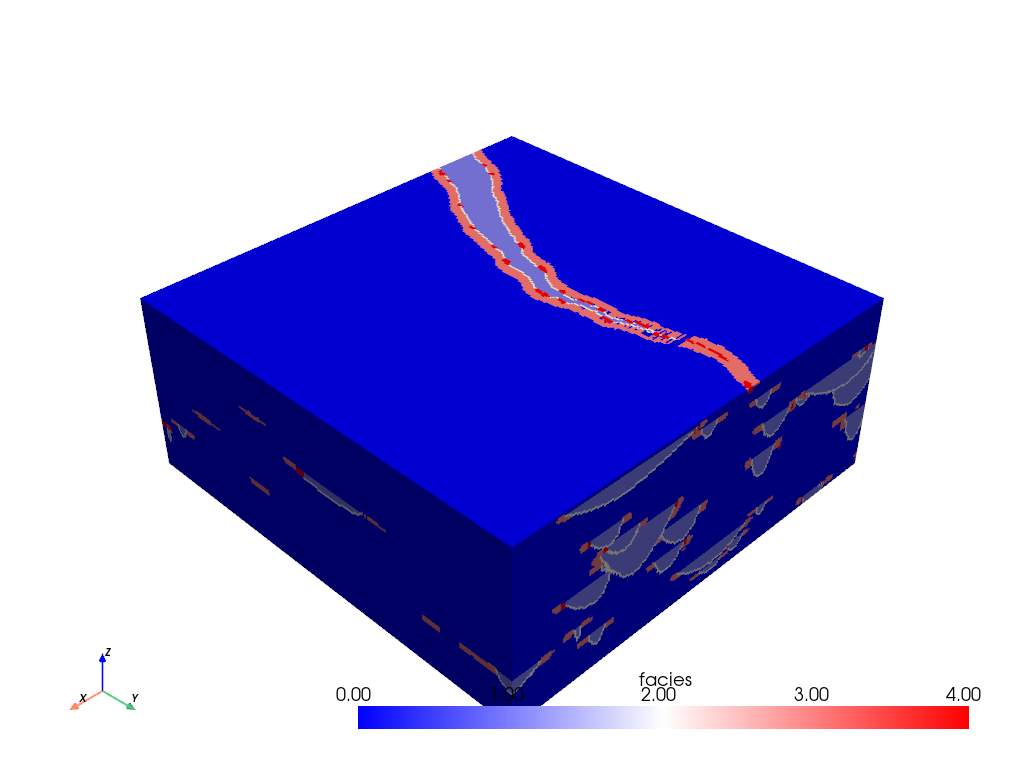
First, let’s load 3D example data from pyvista and plot the only available
dataset: “facies” with a native pyvista plot.
import numpy as np
from pyvista import examples
import ogstools.meshplotlib as mpl
from ogstools.propertylib import Scalar
mpl.setup.reset()
mesh = examples.load_channels()
mesh.plot(cmap="bwr")
data = Scalar("facies", categoric=True)
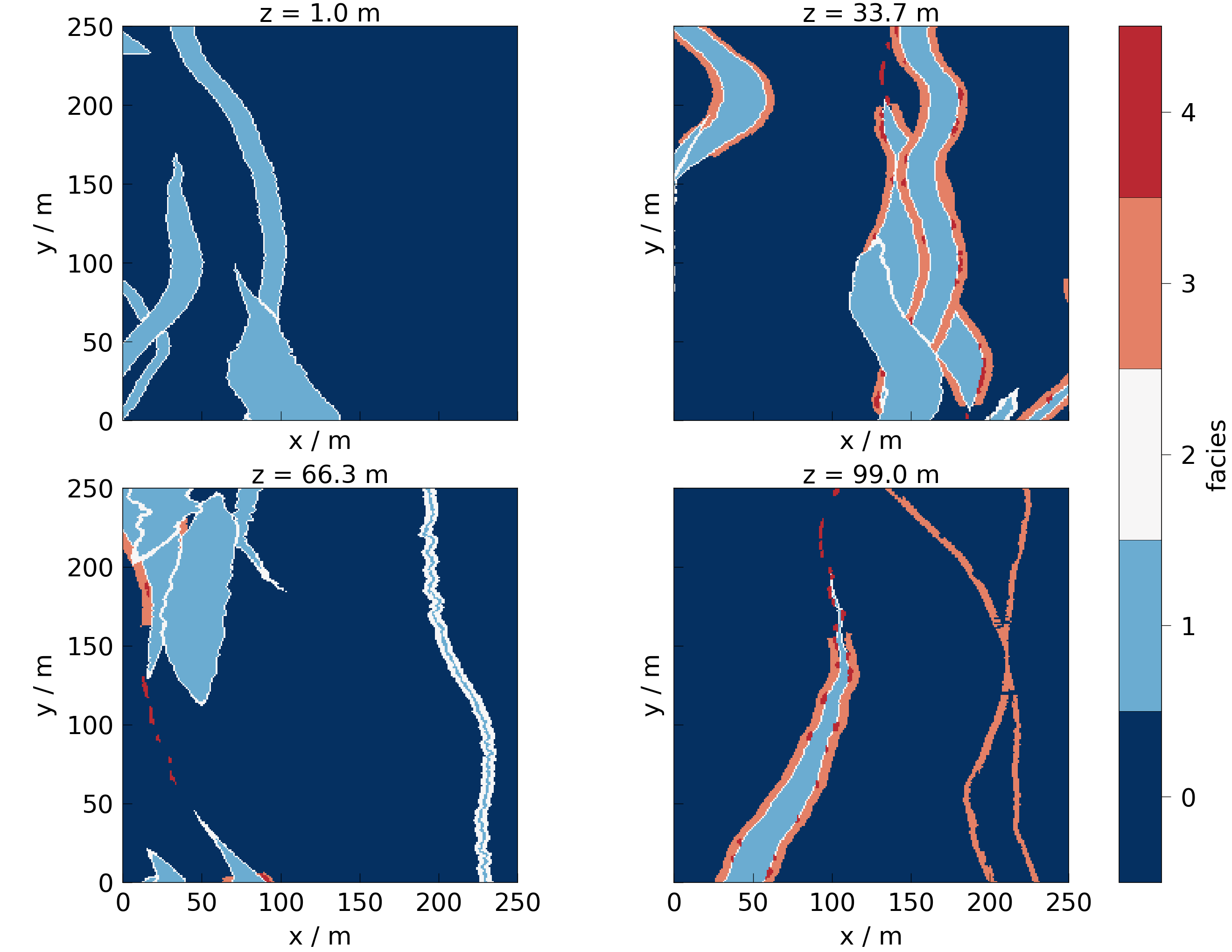
Now, let’s create multiple slices along the z axis and plot them with meshplotlib in a 2 by 2 grid.
slices = np.reshape(list(mesh.slice_along_axis(n=4, axis="z")), (2, 2))
fig = mpl.plot(slices, data)
for ax, slice in zip(fig.axes, np.ravel(slices)):
ax.set_title(f"z = {slice.center[2]:.1f} {mpl.setup.length.data_unit}")
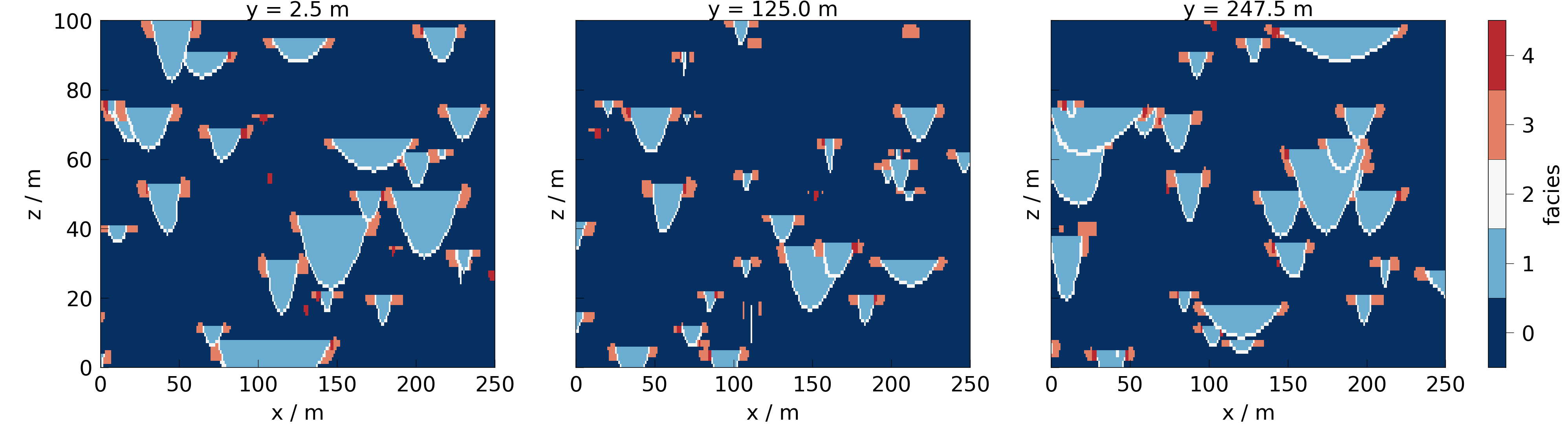
We can also slice along the y-axis and plot the meshes in one row.
slices = np.reshape(mesh.slice_along_axis(n=3, axis="y"), (1, -1))
fig = mpl.plot(slices, data)
for ax, slice in zip(fig.axes, np.ravel(slices)):
ax.set_title(f"y = {slice.center[1]:.1f} {mpl.setup.length.data_unit}")
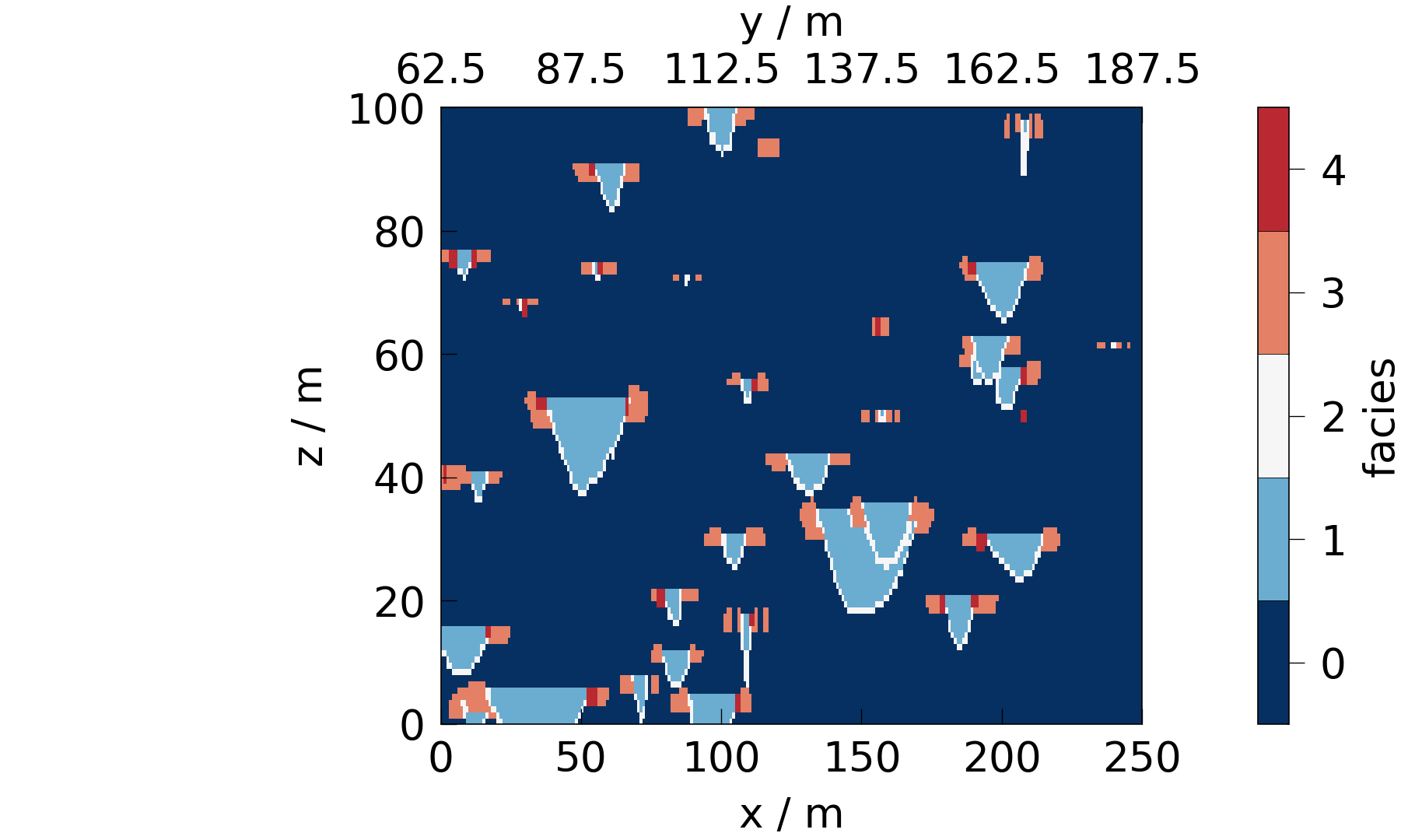
Arbitrary oriented slices are also possible. They get projected to the cardinal plane, from which they have the least rotational offset.
fig = mpl.plot(mesh.slice([1, -2, 0]), data)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 7.530 seconds)