Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Workflow with Feflowlib: Hydraulic model - conversion, simulation and post-processing#
In this example we show how a simple flow/hydraulic FEFLOW model can be converted to a pyvista.UnstructuredGrid and then be simulated in ot.
Necessary imports
import tempfile
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
import ogstools as ot
from ogstools.examples import feflow_model_box_Neumann
from ogstools.feflowlib import (
FeflowModel,
)
1. Load a FEFLOW model (.fem) as a FeflowModel object to further work it. During the initialisation, the FEFLOW file is converted.
temp_dir = Path(tempfile.mkdtemp("feflow_test_simulation"))
feflow_model = FeflowModel(feflow_model_box_Neumann, temp_dir / "boxNeumann")
pv.global_theme.colorbar_orientation = "vertical"
feflow_model.mesh.plot(
show_edges=True,
off_screen=True,
scalars="P_HEAD",
cpos=[0, 1, 0.5],
scalar_bar_args={"position_x": 0.1, "position_y": 0.25},
)
print(feflow_model.mesh)
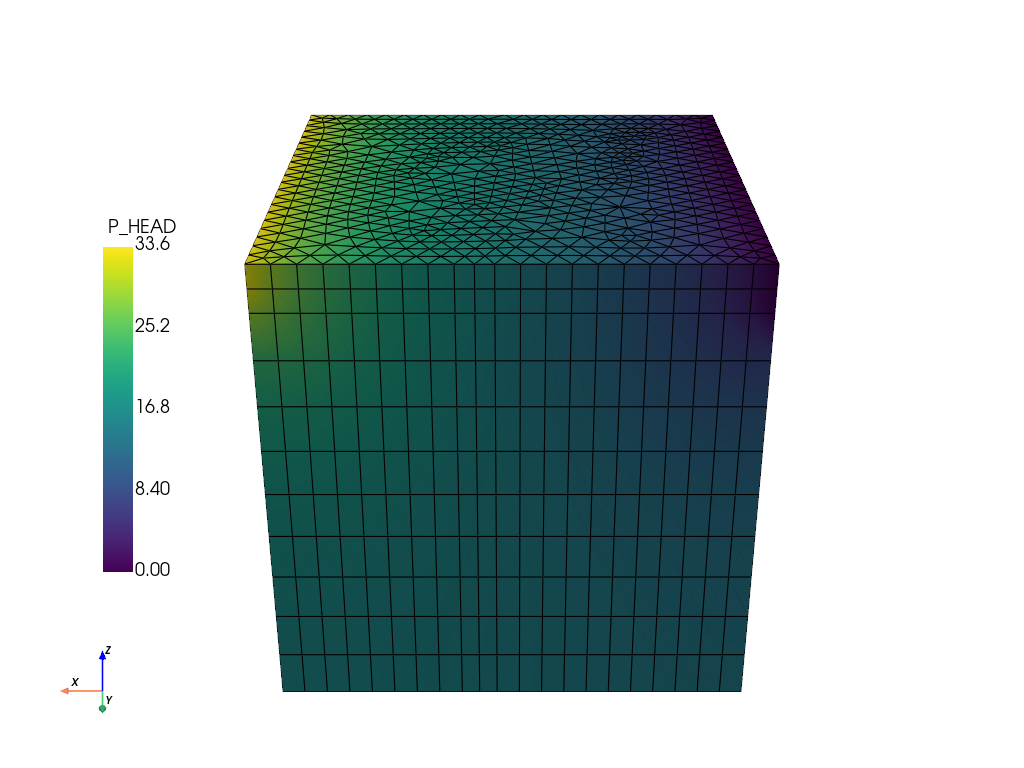
UnstructuredGrid (0x792a98c06aa0)
N Cells: 11462
N Points: 6768
X Bounds: 0.000e+00, 1.000e+02
Y Bounds: 0.000e+00, 1.000e+02
Z Bounds: -1.000e+02, 0.000e+00
N Arrays: 24
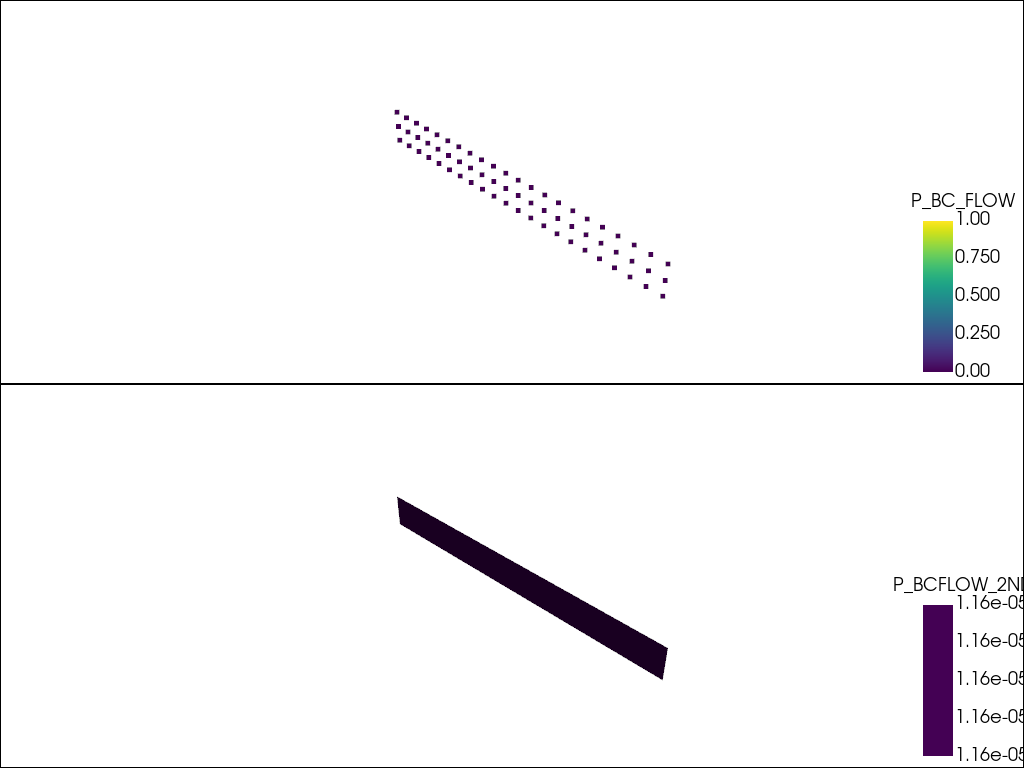
Extract the subdomains conditions.
subdomains = feflow_model.subdomains
# Since there can be multiple boundary conditions in the subdomains,
# they are plotted iteratively.
plotter = pv.Plotter(shape=(len(subdomains), 1))
for i, (name, boundary_condition) in enumerate(subdomains.items()):
# topsurface refers to a cell based boundary condition.
if name != "topsurface":
plotter.subplot(i, 0)
plotter.add_mesh(boundary_condition, scalars=name)
plotter.show()
Define endtime and time stepping in the project-file.
feflow_model.setup_prj(
end_time=int(1e8),
time_stepping=[(1, 10), (5, 100), (10, 1000), (10, 1e6), (1, 1e7)],
)
Run the model
feflow_model.run()
Project file written to output.
Simulation: /tmp/tmp2r7y0ah2feflow_test_simulation/boxNeumann.prj
Status: finished successfully.
Execution took 3.619508981704712 s
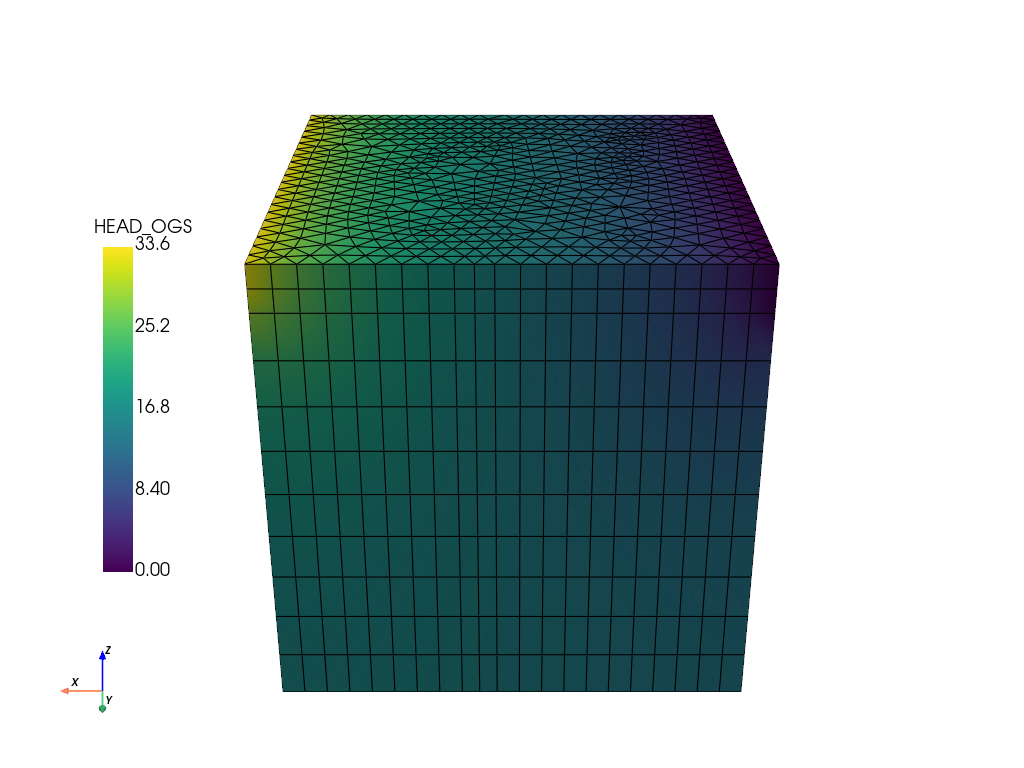
Read the results and plot them.
ms = ot.MeshSeries(temp_dir / "boxNeumann.pvd")
# Read the last timestep:
ogs_sim_res = ms.mesh(ms.timesteps[-1])
"""
It is also possible to read the file directly with pyvista:
ogs_sim_res = pv.read(temp_dir / "boxNeumann_ts_1_t_1.000000.vtu")
"""
ogs_sim_res.plot(
show_edges=True,
off_screen=True,
scalars="HEAD_OGS",
cpos=[0, 1, 0.5],
scalar_bar_args={"position_x": 0.1, "position_y": 0.25},
)
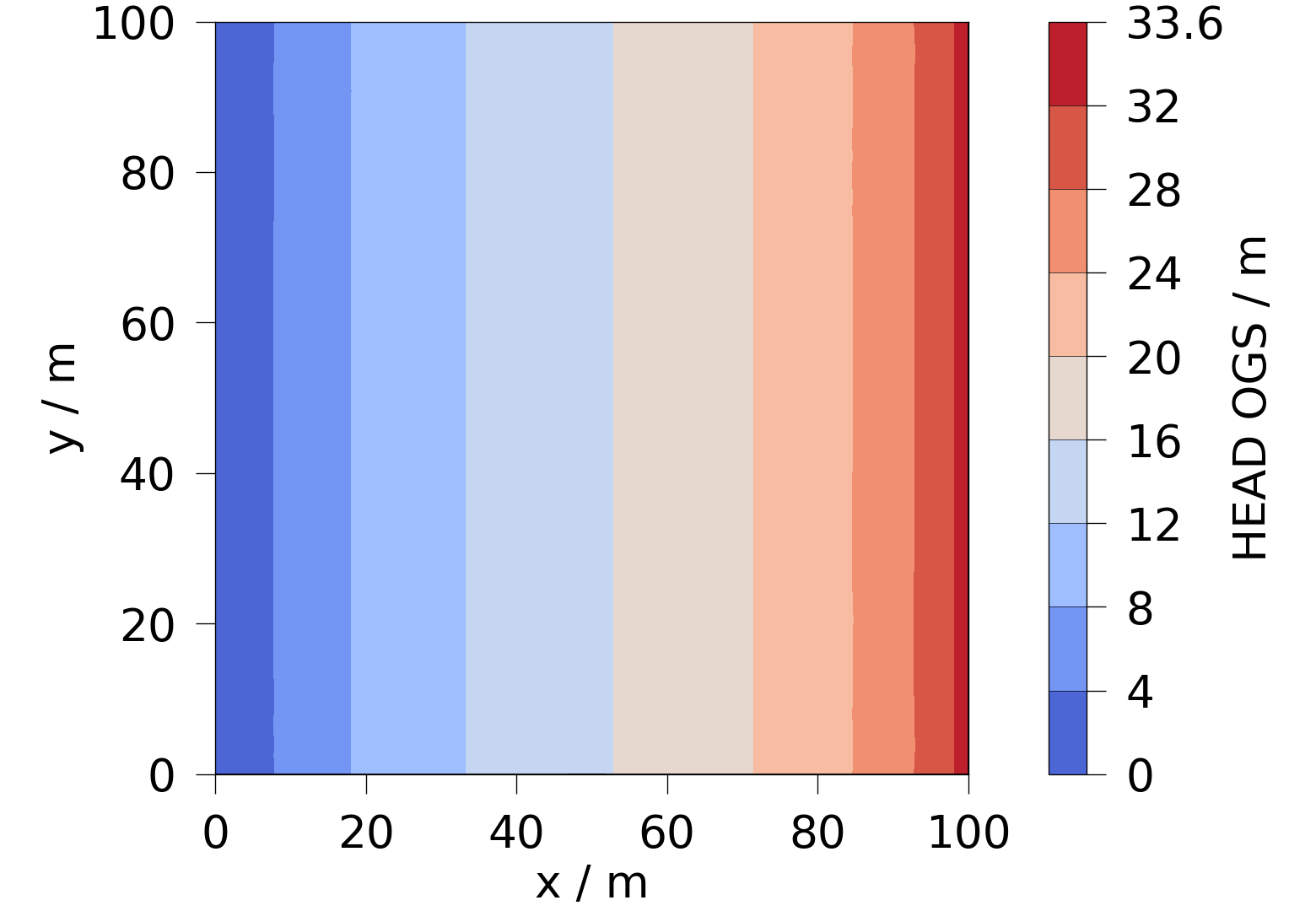
5.1 Plot the hydraulic head simulated in OGS with ogstools.plot.contourf.
head = ot.variables.Scalar(data_name="HEAD_OGS", data_unit="m", output_unit="m")
fig = ot.plot.contourf(ogs_sim_res.slice(normal="z", origin=[50, 50, 0]), head)
Calculate the difference to the FEFLOW simulation and plot it.
diff = feflow_model.mesh["P_HEAD"] - ogs_sim_res["HEAD_OGS"]
feflow_model.mesh["diff_HEAD"] = diff
feflow_model.mesh.plot(
show_edges=True,
off_screen=True,
scalars="diff_HEAD",
cpos=[0, 1, 0.5],
scalar_bar_args={"position_x": 0.1, "position_y": 0.25},
)
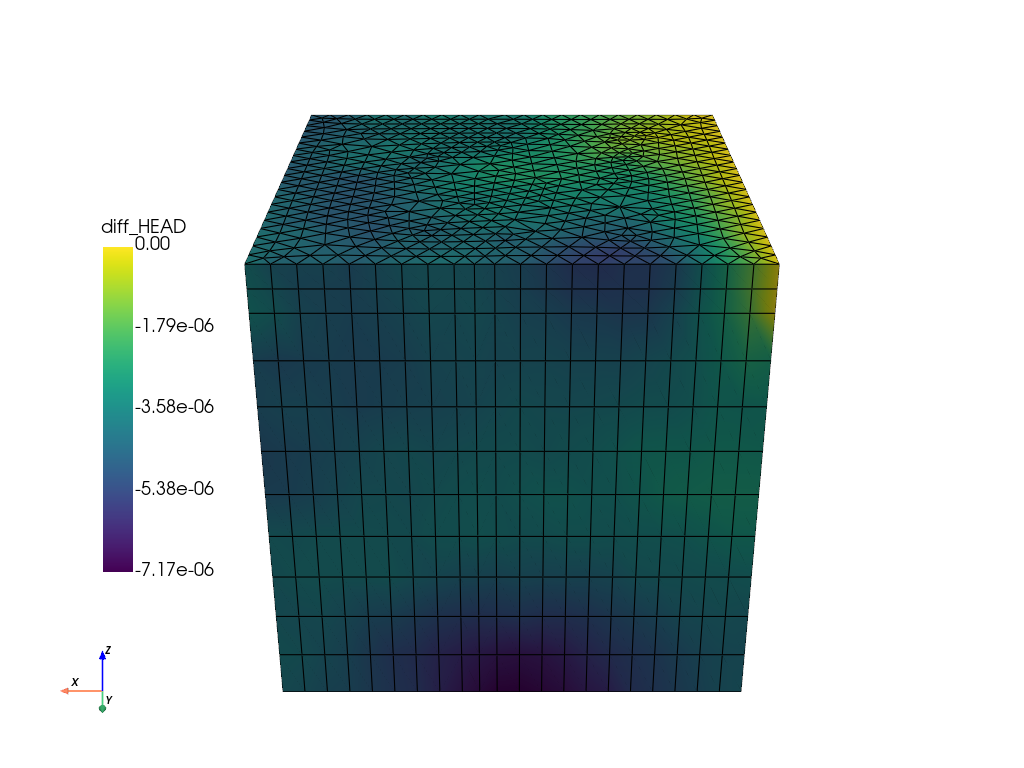
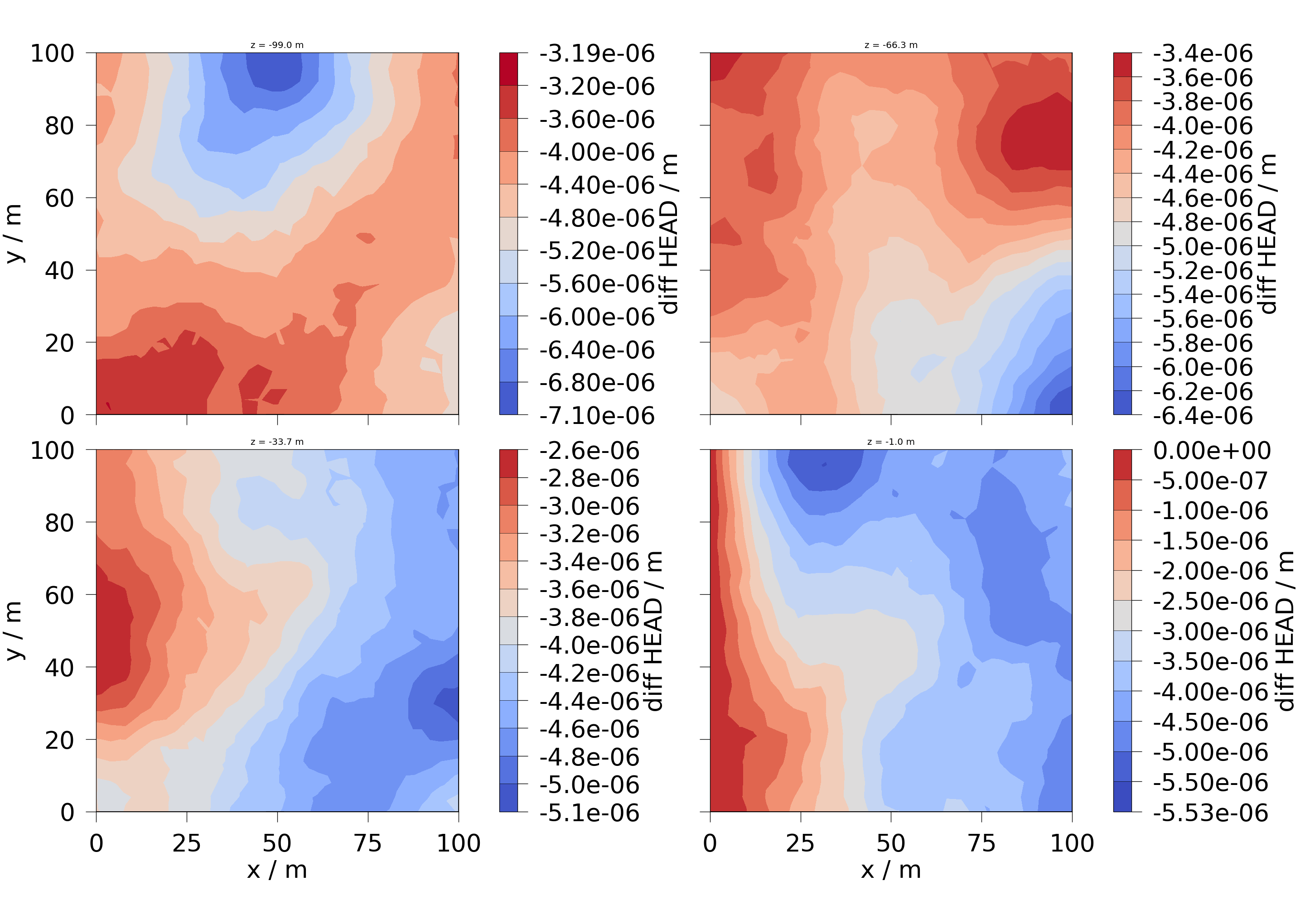
6.1 Plot the differences in the hydraulic head with ogstools.plot.contourf.
Slices are taken along the z-axis.
diff_head = ot.variables.Scalar(
data_name="diff_HEAD", data_unit="m", output_unit="m"
)
slices = np.reshape(
list(feflow_model.mesh.slice_along_axis(n=4, axis="z")), (2, 2)
)
fig = ot.plot.contourf(slices, diff_head)
for ax, slice in zip(fig.axes, np.ravel(slices), strict=False):
ax.set_title(f"z = {slice.center[2]:.1f} m", fontsize=32)
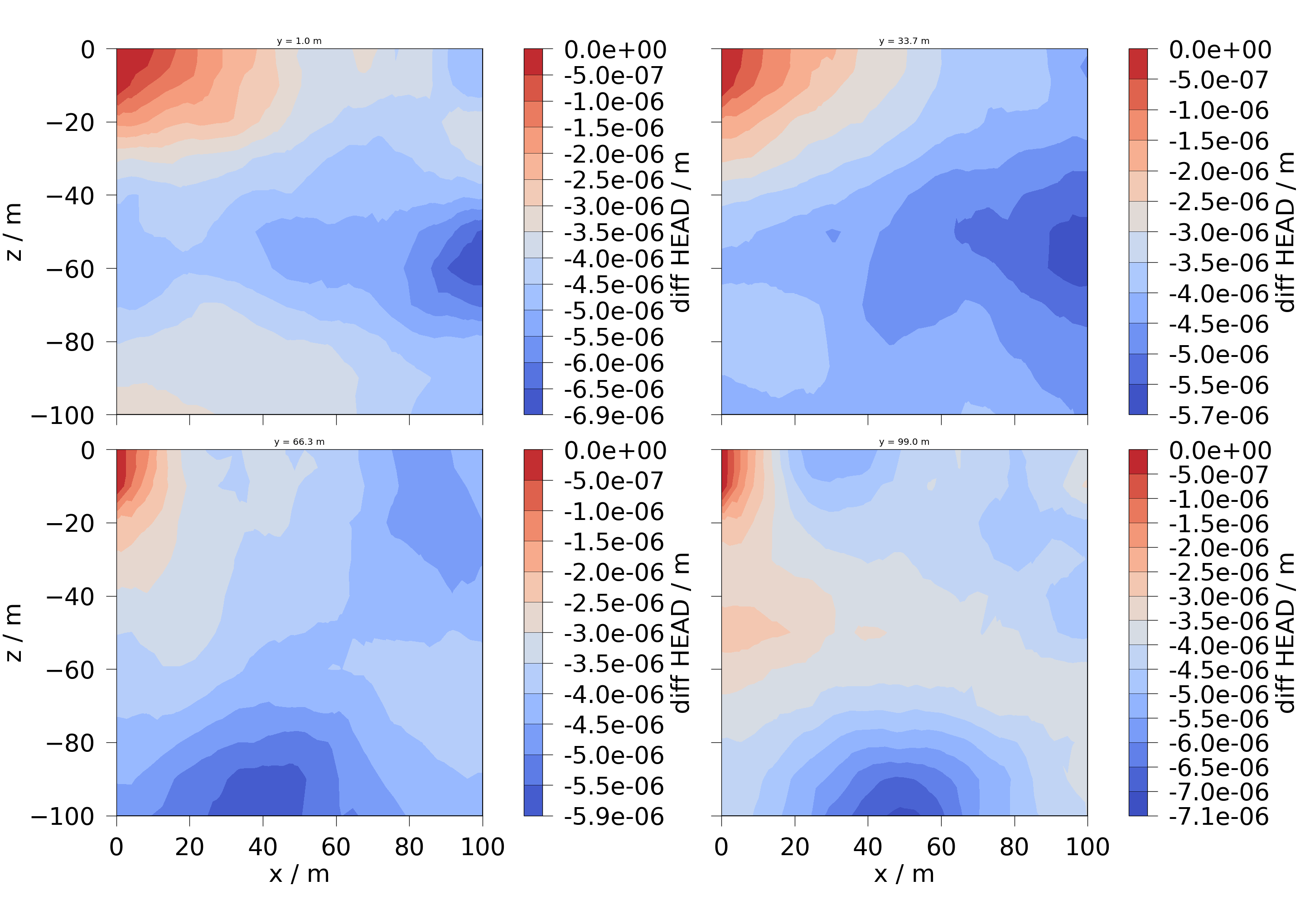
6.2 Slices are taken along the y-axis.
slices = np.reshape(
list(feflow_model.mesh.slice_along_axis(n=4, axis="y")), (2, 2)
)
fig = ot.plot.contourf(slices, diff_head)
for ax, slice in zip(fig.axes, np.ravel(slices), strict=False):
ax.set_title(f"y = {slice.center[1]:.1f} m", fontsize=32)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 9.342 seconds)

